- Download PDF of the report
- Executive Summary
- Introduction
- Chapter 1 – Importance of Freight to Minnesota
- Chapter 2 – Current and Future Freight Trends and Issues
- Chapter 3 – Minnesota’s Freight System Assets, Conditions and Performance
- Chapter 4 – Freight Forecasts
- Chapter 5 – Freight Policies and Strategies
- Chapter 6 – Sustainable Truck Trends and Strategies
- Chapter 7 – Freight Investment Plan and Implementation
- Appendix A – Critical Urban and Rural Freight Corridors
- Appendix B – Freight Performance Measures
- Appendix C – IIJA State Freight Plan Requirements
Appendix B: Freight Performance Measures
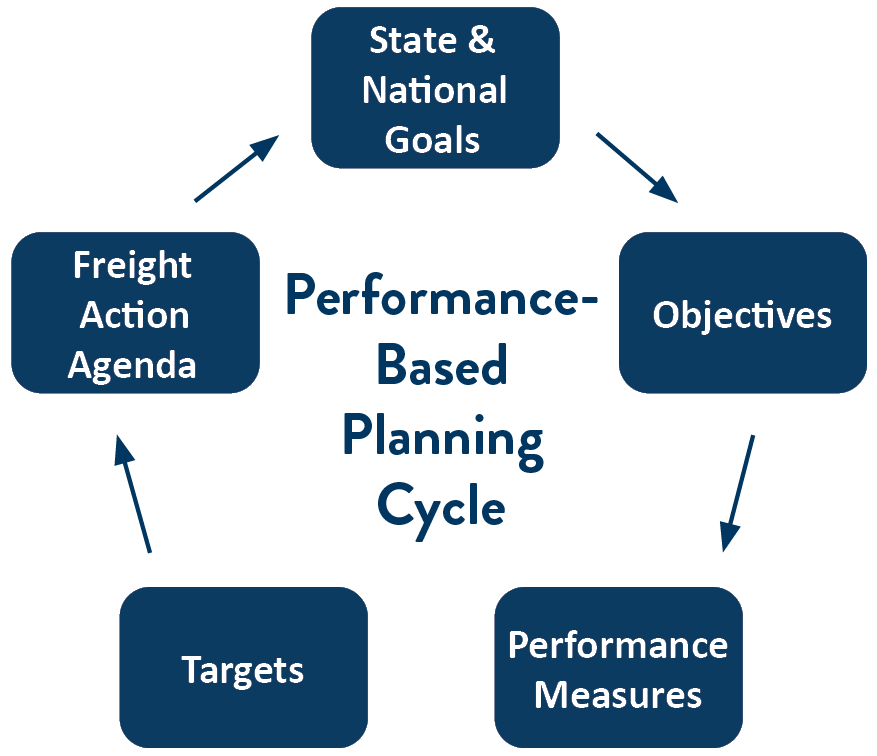
The Minnesota State Freight Plan uses a performance-based planning approach. It includes a review of national freight plan guidance, national freight plan goals, and a review of peer state efforts at developing goals and performance measures.
Components of Performance-Based Planning
- Goals: A goal is a broad statement that describes a desired result or end state. Goals are typically supported by specific objectives.
- Objectives: The result to be achieved. Objectives are more specific than goals and there are often multiple objectives for each goal.
- Performance Measures: A way to quantify progress towards goals.
Multimodal Transportation Goals and Objectives
The State Freight Plan supports the goals identified in the Minnesota Statewide Multimodal Transportation Plan (SMTP). The SMTP is Minnesota’s highest level policy plan for transportation. It is a 20-year plan based on the Minnesota GO Vision for a transportation system that maximizes the health of people, the environment, and economy.
Performance-Based Planning Cycle
State Freight Plan Objectives
- Improve Freight System Safety
- Reduce Freight’s Impact on the Environment
- Minimize Disparate Freight Impacts to Underserved or Overburdened Communities
- Preserve and Improve Minnesota’s Freight Infrastructure
- Improve Freight Mobility, Velocity, and Reliability
- Consideration of All Freight Modes in Planning and Design
- Increase Freight System Resiliency
- Strategically Invest in New Freight Infrastructure
- Support and Grow Minnesota’s Freight Industries
How are Freight Performance Measures Used?
- Description. Describe the effect of an investment, program, or policy.
- Evaluation. Assess progress and determine problems or barriers.
- Accountability. Set targets for specific staff or programs and measure performance.
- Decision-support. Support the most sustainable outcomes.
- Communication. Explain to partners what was achieved.
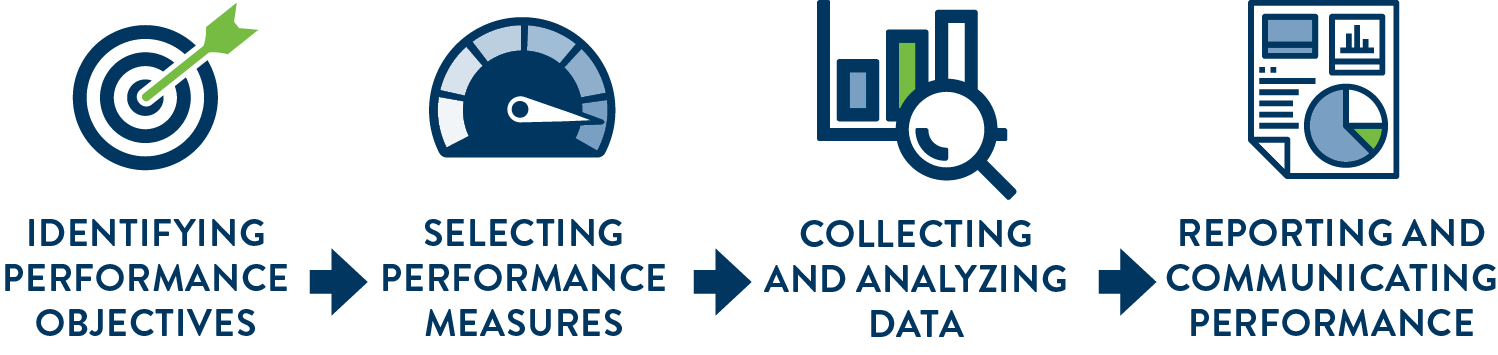
Freight Performance Measurement
The practice of consistently evaluating performance is vital to achieving Minnesota’s identified goals. MnDOT staff regularly measure outcomes and results, which generates reliable data on the effectiveness and efficiency of investments, policies, and programs. By doing this, MnDOT staff maintain an effective methodology for quantifying goals and objectives and communicating progress toward their attainment.
- Identifying Performance Objectives
- Selecting Performance Measures
- Collecting and Analyzing Data
- Reporting and Communicating Performance
State Freight Plan Performance Measures
| SMTP Objectives/Focus Areas | State Freight Plan Objectives | Performance Measures | Actors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Safety / Transportation Safety | Improve Freight System Safety | Combined Freight-Involved Fatalities | MnDOT / NTSB |
| Fatal Truck Crashes | MnDOT / NTSB | ||
| Fatal Truck Crash Rate | MnDOT / NTSB | ||
| Serious Truck Injury Crashes | MnDOT / NTSB | ||
| Serious Injury Truck Crash Rate | MnDOT / NTSB | ||
| Severe Crashes Involving Trucks | MnDOT / NTSB | ||
| RR Crossing Fatalities | MnDOT / NTSB / FRA | ||
| RR Crossing Serious Injuries | MnDOT / NTSB / FRA | ||
| Annual Rail Derailments | MnDOT / NTSB / FRA | ||
| RR Trespassing Incidents | MnDOT / Private Sector / FRA / RR’s | ||
| Rail Grade Crossing Risk | MnDOT / Private Sector / FRA | ||
| Aging Infrastructure / System Stewardship | Preserve and Improve Minnesota's Freight Infrastructure | NHS Pavement in Good Condition | MnDOT |
| Trunk Highway in Good Condition | MnDOT | ||
| NHS Bridge Condition | MnDOT | ||
| Trunk Highway Bridge Condition | MnDOT | ||
| NHS Culvert Condition | MnDOT | ||
| Airport Pavement Condition | MnDOT / Private Sector | ||
| Ports, Locks, Dams Service Life | MnDOT / USACE | ||
| Strategically Invest in New Freight Infrastructure | Funding Allocated (New or Expanded Freight Infrastructure) | MnDOT | |
| Climate / Climate Action | Reduce Freight's Impact on the Environment | Age of Registered MN Trucks | MnDOT/ Private Sector / MN DPS |
| Age of MN Truck Fleet | MnDOT/ Private Sector | ||
| Zero Emission Medium/Heavy Duty Vehicles | MnDOT / Private Sector | ||
| HCAADT Vehicle-Mile Proximity to Alternative Fuel Stations | MnDOT | ||
| Wildlife Habitat Loss | MnDOT / Local Municipalities | ||
| Mode Shift | TBD | ||
| Dwell Time | TBD | ||
| Increase Freight System Resiliency | Freight Resiliency to Severe Weather Events | MnDOT | |
| Economy and Employment | Support and Grow Minnesota's Freight Industries | Freight Employment by Industry | MnDOT / DEED / Private Sector |
| Freight Tonnage by Mode | MnDOT / FHWA | ||
| Freight Value by Mode | MnDOT / FHWA | ||
| Proximity to Freight Facilities | MnDOT | ||
| Intermodal Container Lifts | MnDOT | ||
| Cost of Transportation | TBD / Private Sector | ||
| Empty/Deadhead Truck Miles | TBD | ||
| Critical Connections | Improve Freight Mobility, Velocity, and Reliability | Truck Travel Time Reliability | MnDOT |
| Roadway Truck Bottlenecks | MnDOT | ||
| Hours of Delay | MnDOT | ||
| Truck Speed | MnDOT | ||
| OSOW Barriers Removed | MnDOT | ||
| Truck Ton Miles | MnDOT | ||
| Equity / Healthy Equitable Communities | Minimize Disparate Freight Impacts to Underserved or Overburdened Communities | Population in Designated Food Deserts | MnDOT / State Demographer / MN Federal Reserve |
| Workforce Participation Rate | MnDOT / DEED | ||
| Freight Investment in Justice40 Areas | MnDOT | ||
| Freight GHG Emissions Impacts | MnDOT / MN GHG Emissions Impact Mitigation Working Group | ||
| Concentrations and Levels of Air Pollutants Near EJ Communities | MnDOT / EPA | ||
| Freight Workforce Demographics | MnDOT / DEED | ||
| Quantity and Freight Volumes of Parcel Aggregation, Micro Hubs, and Similar Infrastructure | MnDOT / Local Municipalities | ||
| Transportation Options | Consideration of All Freight modes in Planning and Design | Proportion of City, County, and Regional Transportation Studies and Plans Including Consideration of Freight Modal Issues | MnDOT / Local Municipalities, Met Council |
